The list of unanswered questions in science 2025 isn’t just a catalog of what we don’t know; it’s a treasure map. It points to the frontiers of human knowledge, where the next monumental discoveries—and potentially, the next Nobel Prizes—are waiting to be found. If you’ve ever dreamed of contributing something truly fundamental to our understanding of the universe, this map is for you. This article will guide you through the biggest scientific mysteries of our time, not just as abstract puzzles, but as tangible opportunities for the curious and the bold.

unanswered questions in science 2025
| Field of Study | Grand Challenge | Potential Nobel-Winning Impact |
| Cosmology & Physics | What are dark matter and dark energy? | Unveiling the true composition of 95% of the universe, rewriting cosmic models. |
| Neuroscience | What is the biological basis of consciousness? | Solving the “hard problem” of how physical brains create subjective experience. |
| Biology & Chemistry | How did life on Earth originate? | Creating life from non-living matter in a lab, confirming the theory of abiogenesis. |
| Theoretical Physics | How can we unify general relativity and quantum mechanics? | Developing a “Theory of Everything” that governs all physical laws, from black holes to subatomic particles. |
The Cosmos: Our Place in the Universe
For millennia, we have looked to the stars for answers. Today, our powerful instruments have revealed that the cosmos is far stranger and more mysterious than our ancestors ever imagined. The biggest questions out there challenge the very foundations of physics.
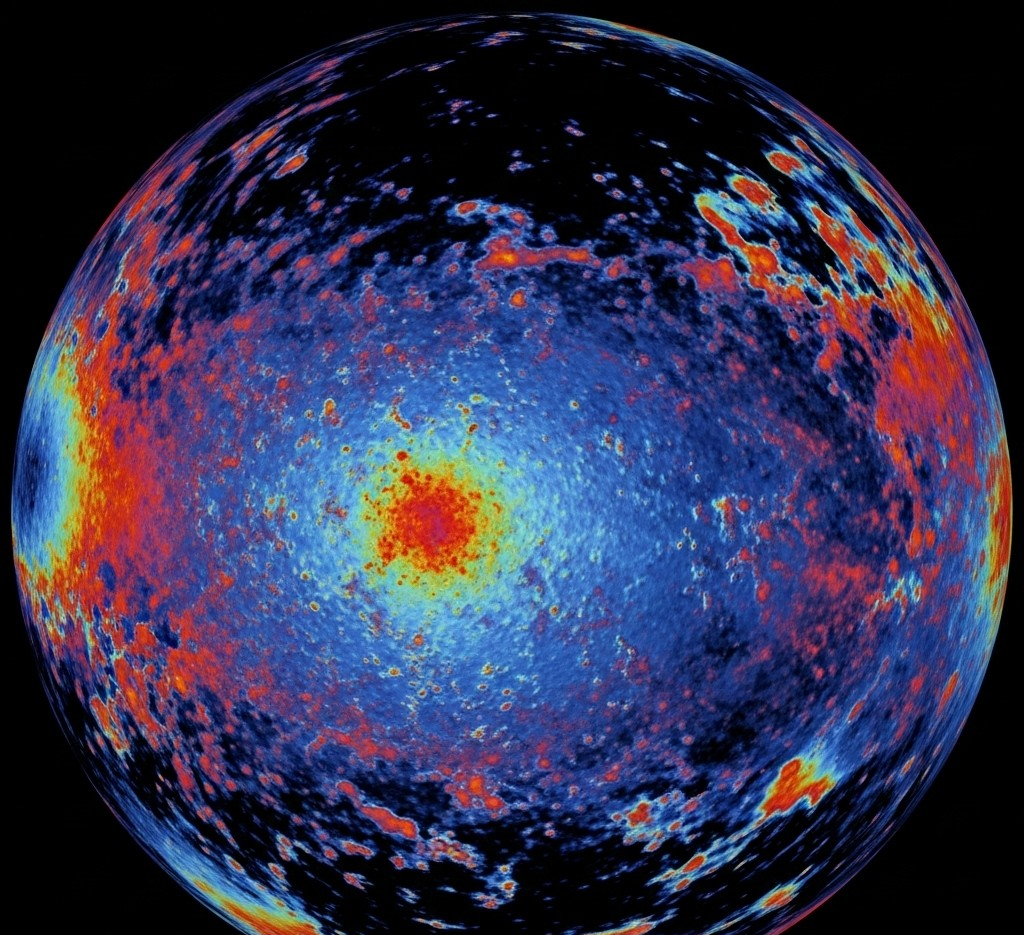
What are Dark Matter and Dark Energy?
You, me, the stars, and the galaxies—everything we can see and touch—make up less than 5% of the universe. The rest is a profound enigma. About 27% is dark matter, an invisible substance whose gravitational pull prevents galaxies from flying apart. Another 68% is dark energy, a mysterious force that is causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate.
According to NASA, we know more about what dark matter isn’t than what it is. It isn’t ordinary matter, nor is it the antimatter we can create in labs. Solving this would not just be a discovery; it would be like finding the missing pages from the instruction manual of the cosmos.
Are We Alone? The Search for Extraterrestrial Life
The question of alien life has moved from science fiction to a serious scientific discipline known as astrobiology. With the discovery of thousands of exoplanets, many in the “habitable zone” of their stars, the odds seem to be tilting in favor of life existing elsewhere. The James Webb Space Telescope is already analyzing the atmospheres of these distant worlds for biosignatures—gases like oxygen or methane that could indicate biological processes.
Finding any life, even microbial, beyond Earth would fundamentally change our place in the universe. It would prove that the origin of life is not a one-off fluke, shifting our perspective on our own existence.
The Code of Life: Mysteries Within Ourselves
While we look to the stars, some of the most profound unanswered questions lie within our own biology. From the dawn of life to the nature of the mind, these mysteries are deeply personal.
How Did Life on Earth Begin?
We understand evolution well, but the spark that started it all—the transition from a chemical soup of non-living molecules to the first self-replicating organisms—is still one of the biggest scientific mysteries. This process, called abiogenesis, is a puzzle involving chemistry, geology, and biology. Scientists are exploring theories from deep-sea hydrothermal vents to shallow volcanic ponds, but no one has yet managed to create life from scratch in a laboratory. The first person to do so will have answered one of humanity’s oldest questions.
What is Consciousness?
You are having an experience right now. You see these words, feel the air around you, and have inner thoughts. This subjective awareness is consciousness. But how does a three-pound lump of tissue—your brain—generate it? This is often called the “hard problem.”
Neuroscientists can point to which parts of the brain are active when we feel happy or sad, but they can’t explain why a pattern of firing neurons should feel like anything at all. In my experience covering breakthroughs, this is the field where science and philosophy meet, and a solution would revolutionize everything from artificial intelligence to medicine and our definition of self.
The Quantum Realm: The Strangeness of Reality
On the smallest scales, the universe operates by a set of rules that defy our everyday intuition. This is the world of quantum mechanics, and it holds the key to a deeper understanding of reality itself.
How Can We Unify Gravity and Quantum Mechanics?
Physics has two incredibly successful theories. General relativity perfectly describes the universe on a large scale (planets, stars, gravity). Quantum mechanics perfectly describes it on a small scale (atoms, particles). The problem? They are mathematically incompatible. They simply don’t work together.
Finding a “Theory of Everything,” a single framework that unifies these two pillars of modern physics, is the holy grail for theoretical physicists. String theory and loop quantum gravity are two leading contenders, but a definitive, testable answer remains one of the greatest unsolved problems in physics. The person who cracks this will be the Einstein of our time.
From Insight to Impact: A Nobel Laureate’s Mindset
Tackling these grand challenges requires more than just intelligence. I’ve seen many brilliant researchers, but those who make legendary contributions often share a particular mindset. If you’re aiming for one of these future Nobel Prize topics, cultivating these habits is as crucial as mastering the science.
- Think Interdisciplinarily: The answer to the origin of life won’t come from just a biologist. It will require a chemist, a geologist, and a physicist working together. The lines between scientific fields are blurring, and the biggest discoveries are happening at the intersections.
- Embrace Failure as Data: The path to a Nobel Prize is paved with failed experiments. Each “failure” is not a dead end but a new piece of information that rules out a possibility. It’s a process of elimination on a grand scale. Persistence in the face of repeated setbacks is a non-negotiable trait.
- Communicate and Collaborate: Science is not a solitary pursuit. The days of the lone genius in a dusty lab are largely over. Breakthroughs come from sharing ideas, challenging assumptions, and building on the work of a global community.
Your Journey to Discovery Starts Now
The unanswered questions in science 2025 are daunting, but they are also a profound invitation. Every one of them represents an opportunity for a dedicated mind to peel back another layer of reality and show us all something new about our world.
You don’t need to have all the answers to begin. All you need is a powerful question and the relentless curiosity to pursue it. The names we celebrate in Stockholm weren’t born laureates; they were born curious. Your journey starts not in a grand laboratory, but with the simple, powerful act of asking, “Why?”
John Lions Computer Science Honours Scholarship 2026: From Students to Silicon Valley
Unlocking Your PhD Dream: A Guide to University of Sussex Commonwealth Scholarships 2026
FAQs
Q1:What is the most likely field for the next big scientific breakthrough?
Many experts point toward the intersection of artificial intelligence and biology. Using AI to model protein folding, analyze genetic data, and design new drugs is accelerating research at an unprecedented rate. Fields like personalized medicine and neuro-engineering could see Nobel-worthy breakthroughs in the coming decade.
Q2:How long does it take for a discovery to win a Nobel Prize?
It often takes decades. The Nobel Committee is famously cautious, waiting until a discovery has been thoroughly verified and its impact is widely understood. According to the Nobel Prize’s own data, the average time lag between discovery and prize can be 20-30 years, though this varies.
Q3:Can you win a Nobel Prize for a theoretical idea?
Yes, but it’s rare. The prize is typically awarded for a “discovery” or “invention.” A theoretical idea usually needs to be confirmed by experimental evidence before it is considered. Peter Higgs, for example, proposed the Higgs boson in 1964 but didn’t receive the prize until 2013, after its existence was confirmed at CERN.










